sitthiphong // Shutterstock
8 of the greatest risk factors for heart disease
In the U.S., heart disease kills someone every 36 seconds and is the cause of 25% of all deaths. About 659,000 Americans die from heart disease annually, making it the leading cause of death across most racial groups, regardless of gender.
The most common type of heart disease among Americans is coronary artery disease, which decreases blood flow to the heart. The condition can cause heart attacks and even lead to heart failure.
There are a lot of lifestyle factors that can increase your chances of developing heart disease like excessive body weight, smoking, and drinking too much. Fortunately, there are many ways to reduce your risk of heart disease as well, such as staying active, following a low-fat diet, and maintaining a healthy weight. In fact, according to the American Heart Association and the Cleveland Clinic, 80% to 90% of heart disease may be preventable.
ACLS Medical Training researched how eight major risk factors can lead to heart disease, citing the CDC.
Andrey_Popov // Shutterstock
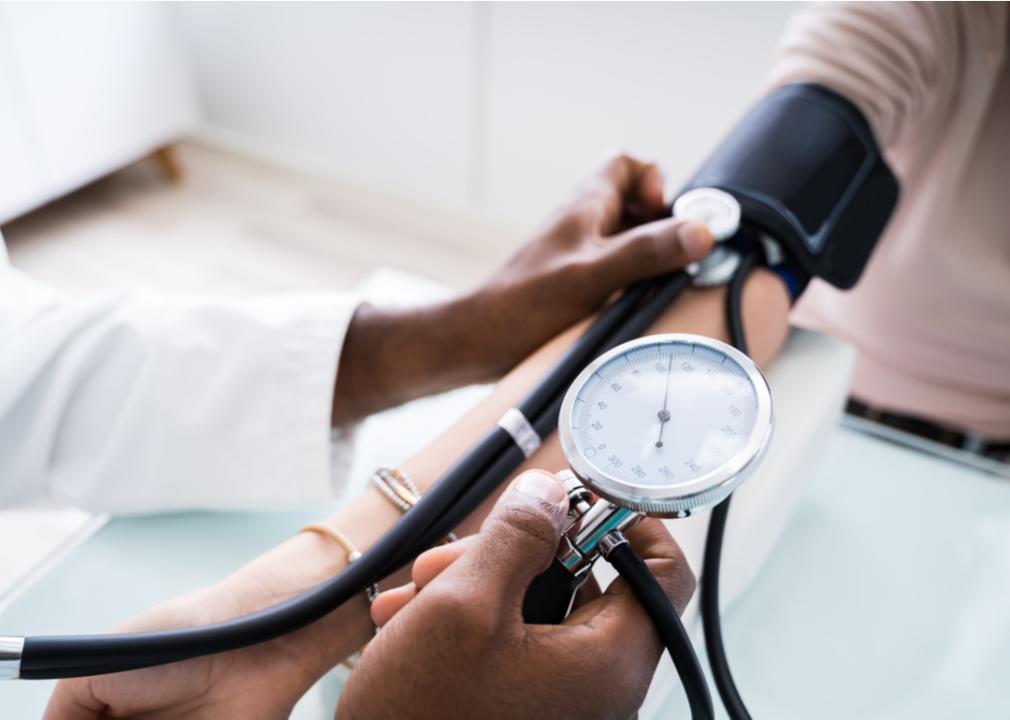
High blood pressure
High blood pressure not only increases your risk for heart disease, but it can also lead to strokes. Unfortunately, high blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common issue in Americans, affecting half the adults in the country.
Many struggle to control their hypertension and it’s estimated that only 1 in 4 adults with high blood pressure are managing their condition through lifestyle changes and medication. To better control your risk for heart disease, check your blood pressure regularly. This simple measurement can be done by a physician or with an at-home blood pressure monitor. You can take steps to control your high blood pressure by exercising consistently and eating a diet low in fat. If you’re seeing a physician for your high blood pressure, be sure to follow their instructions and don’t stop taking any medication they prescribe without consulting them first.
Jarun Ontakrai // Shutterstock
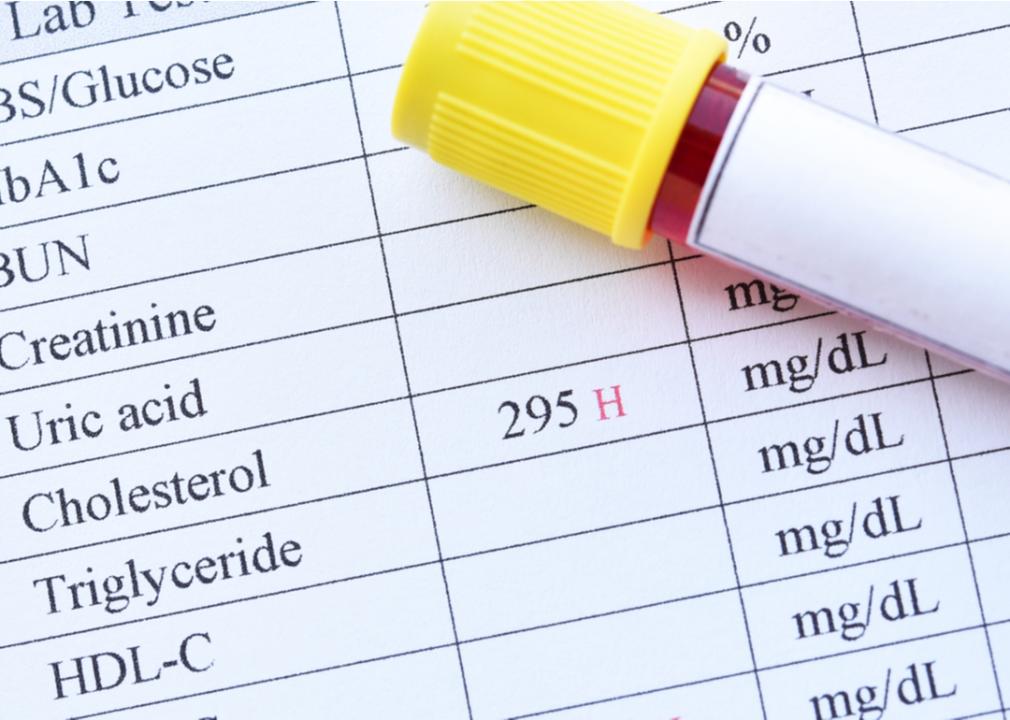
High blood cholesterol
According to the CDC, roughly 38% of Americans live with high cholesterol. Cholesterol can come from two sources: blood cholesterol (which is produced by your liver) and dietary cholesterol (which comes from consuming meat, seafood, or dairy products). High cholesterol can stem from a number of risk factors including family history, smoking, physical inactivity, being overweight, Type 2 diabetes, and a diet that contains a lot of trans and saturated fats. To avoid high blood cholesterol, you can limit alcohol intake, stop smoking, eat a balanced diet, and stay physically active. If you’re living with high cholesterol, consult with your physician for medication options, monitor your cholesterol, and stick to a healthy diet and exercise.

fongbeerredhot // Shutterstock
Smoking
It’s no secret that smoking is bad for your health—yet, as of 2019, 34.1 million Americans regularly smoked cigarettes. Like high blood cholesterol and blood pressure, smoking tobacco can put you at high risk for heart disease. It can also lead to an addiction to tobacco, so quitting can be challenging. Counseling and medication can help you break your addiction and manage withdrawal symptoms. You can use nicotine patches, gum, and lozenges as well as prescription nasal sprays and inhalers.

fizkes // Shutterstock
Diabetes
Diabetes occurs when your body can’t move sugar from your bloodstream into cells. It’s a chronic issue and is a serious health condition that impacts millions of people annually.
There are several types of diabetes including Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and prediabetes. Typically, those who are overweight, over the age of 45, and have a family history of diabetes are at the greatest risk for developing Type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, diabetes does not have a cure, but treatments are available. Exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, and managing your weight can help to maintain healthy blood glucose levels. Regularly checking in with your physician is also an important aspect of living with diabetes.

mojo cp // Shutterstock
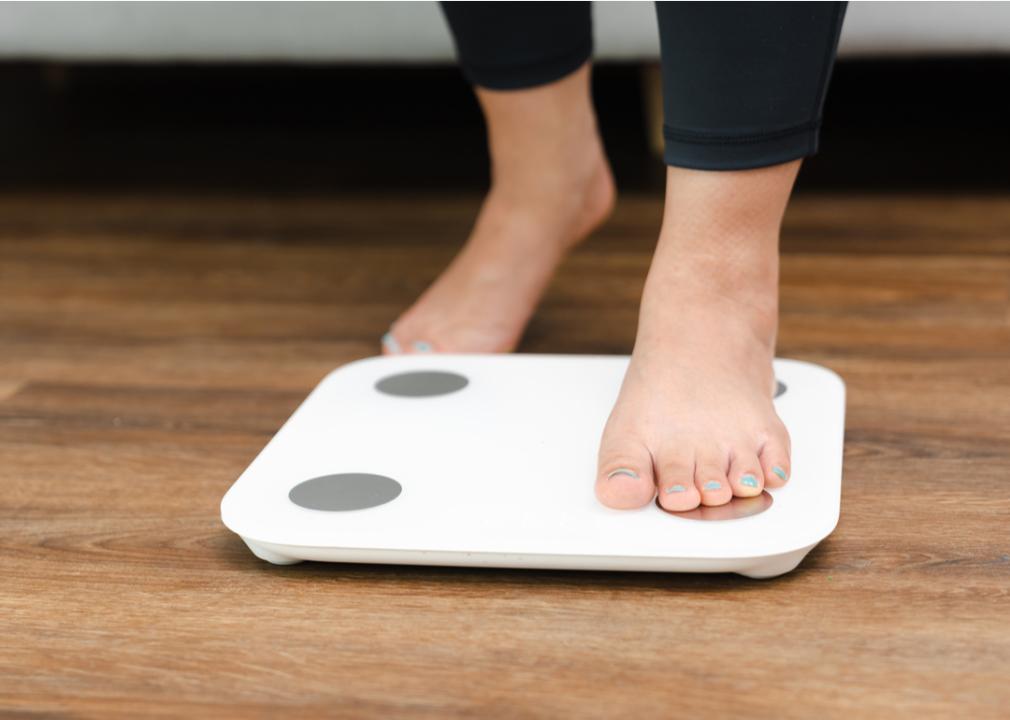
Obesity
Excessive weight gain can lead to a host of chronic health issues, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. However, being overweight is a complex problem that can stem from a number of issues ranging from genetics and health issues to diet and exercise.
Maintaining a healthy weight can start with consulting with your physician and a nutritionist. Both can help you develop strategies to create and stick with a nutritious eating plan. Being physically active can also help with managing your weight. The CDC recommends that most adults get 150 minutes of exercise per week, and this activity should include aerobics (like walking or swimming) and strengthening your muscles.

Stokkete // Shutterstock
Physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is a widespread issue across the U.S., but particularly in Alabama, Arkansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Oklahoma, and West Virginia. When surveyed, more than 30% of adults from these states said they did not participate in any physical activities outside their job in the last month. An active lifestyle can not only help you avoid issues like heart disease and Type 2 diabetes, but it can help you live longer and improve your mental health.
To learn more about becoming more physically active, talk to your physician. You can also take steps like joining a gym and working with a fitness instructor. Or you can add more activity into your daily routine, like taking walks on your lunch break, using the stairs instead of the elevator, or biking to work instead of driving (if possible).

LightField Studios // Shutterstock
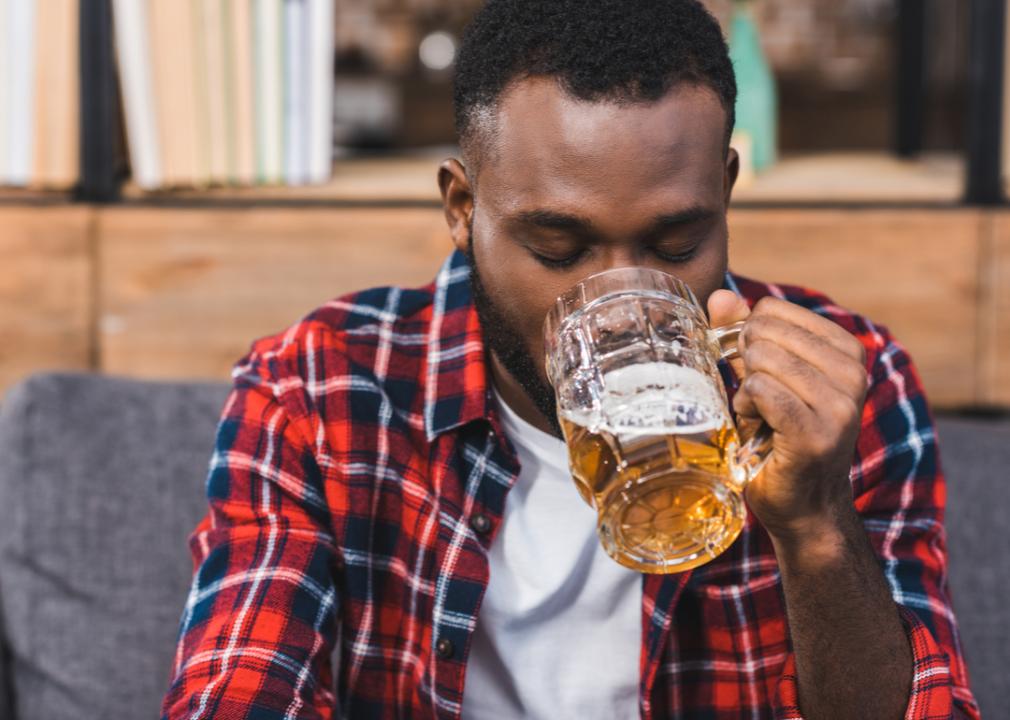
Excessive drinking
While some believe that a glass of red wine a day is good for your heart, consuming too much alcohol can lead to a host of negative health effects. Heavy drinking is hard on your body; not only can it result in heart disease, but it can weaken your immune system and increase the risk of cancer, stroke, high blood pressure, alcohol poisoning, and more.
Drinking excessively is also known as binge drinking, which the CDC defines as four or more drinks for women and over five for men. Drinking too much alcohol can also lead to addiction or even risky behaviors such as driving while intoxicated. To avoid long- and short-term health risks, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans advises adult women to have no more than one drink a day and for men to only have two drinks or less.

Canva
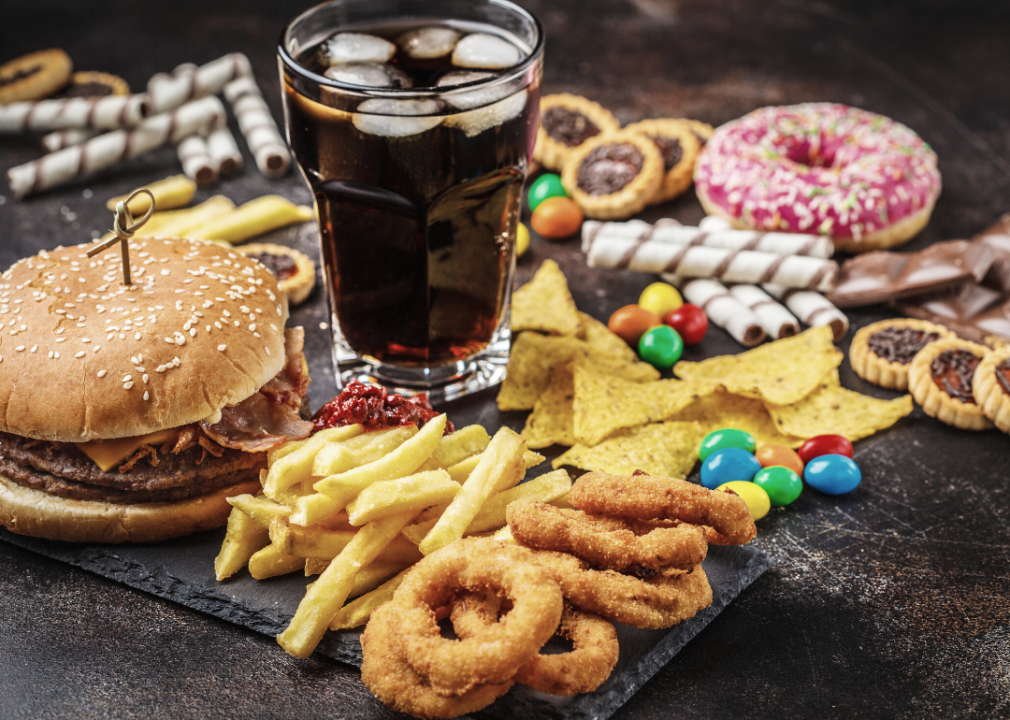
Unhealthy diet
Knowing what foods to eat and how much of it to eat can be confusing, but the CDC recommends that the more naturally colorful your plate, the better.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend that adults limit their daily caloric intake and eat a variety of proteins, vegetables, and whole grains. It’s also important to incorporate lots of fiber, minerals, and vitamins into your diet, which you can find in dark green vegetables, nuts, and fruit. You’ll want to limit sugars, salt, and alcoholic beverages. However, it’s important to keep in mind that it’s beneficial to maintain balance and enjoy comfort foods in moderation.