Multiple Choice
An elderly (82 year old), diabetic woman presents to the emergency department with an episode of syncope. She has a head laceration, but her neurological exam is unremarkable. The woman denies experiencing any symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia prior to the event. She also denies any chest pain, discomfort, or palpitations.
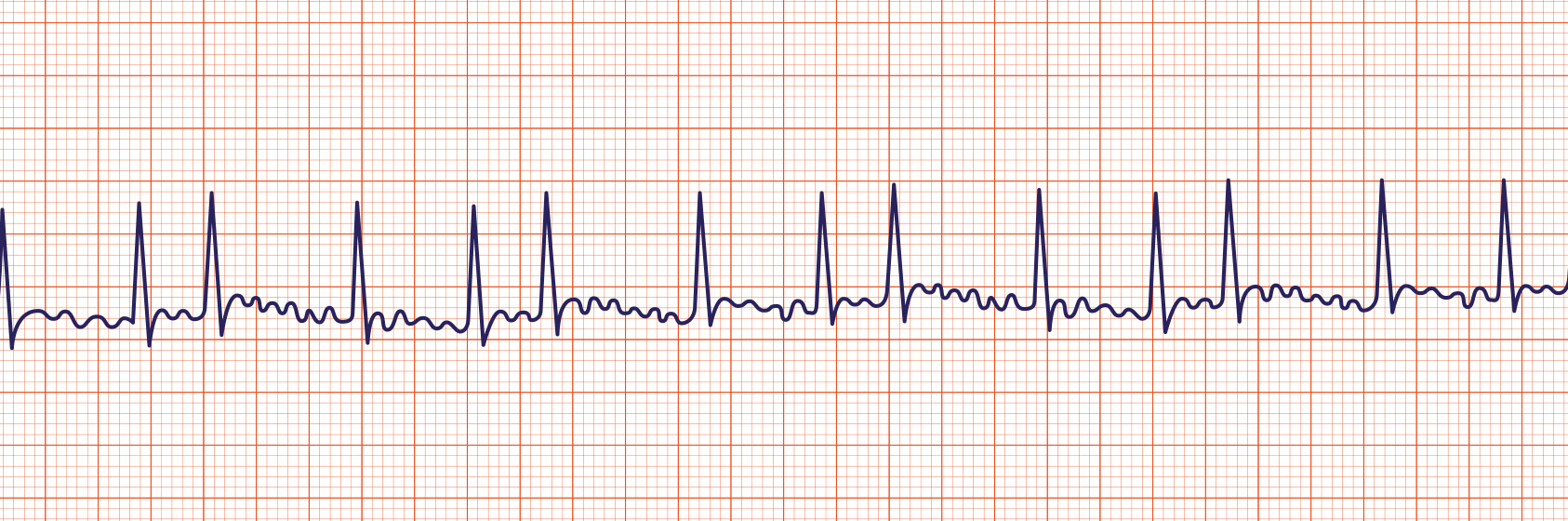
An ECG is obtained:
Which of the following is the most prudent first course of action?
- A. Immediate synchronized cardioversion
- B. Immediate unsynchronized cardioversion
- C. Pharmacological cardioversion (Rhythm control)
- D. Pharmacological cardioversion (Rate control)
- E. Anticoagulation
E. Anticoagulation.
This woman has atrial fibrillation of unknown duration. By calculating her CHA2DS2-VASc Score, one can see that she needs anticoagulation before cardioversion because her thromboembolic stroke risk is unacceptably high (mostly because of her age, gender, and diabetes history).