ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Algorithm
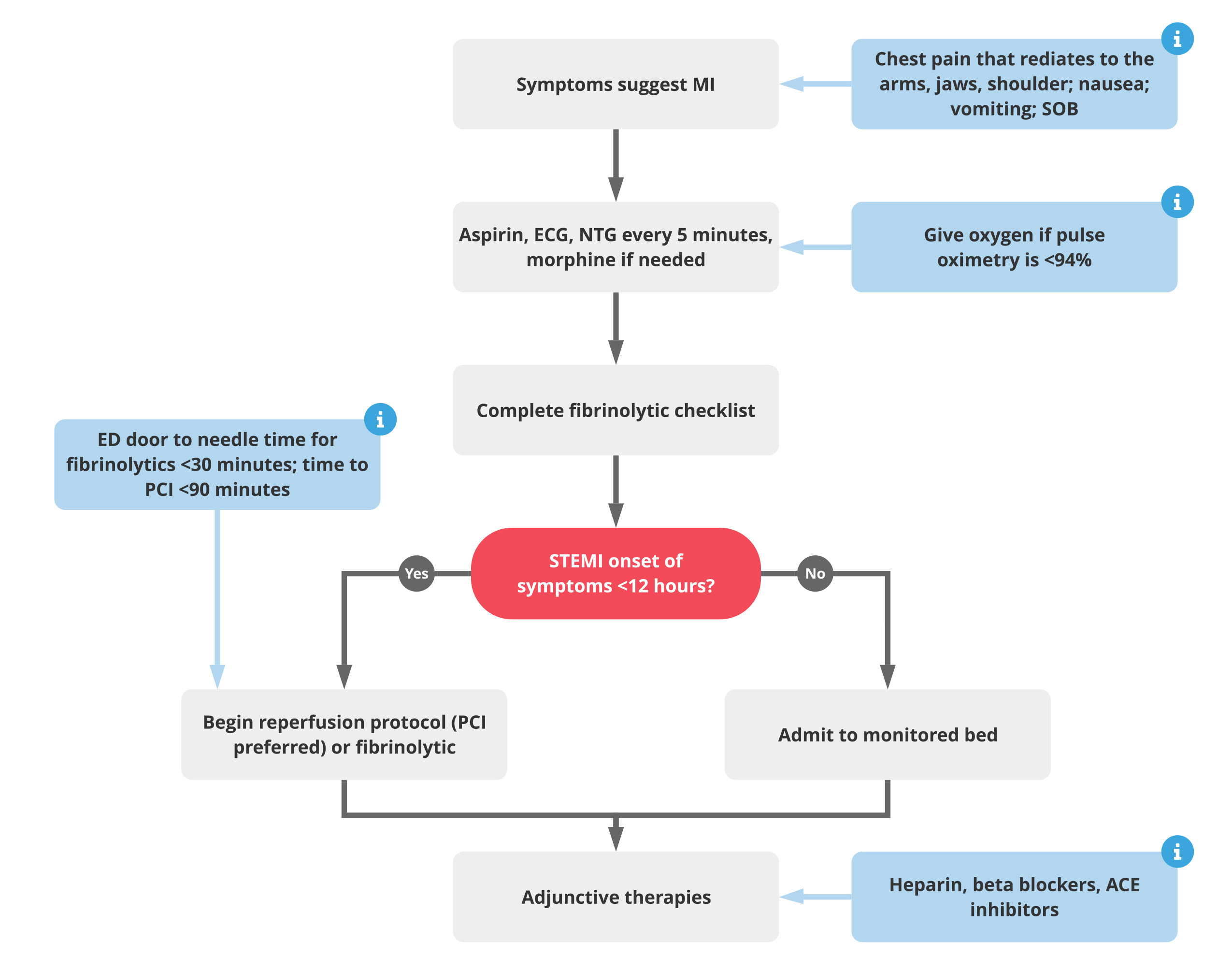
1. Assess patient for symptoms of acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
- Crushing chest pain
- Pain radiates to jaw, arm, back
- Nausea/vomiting
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath
2. Rapid sequence of interventions and additional assessments
- If no aspirin allergies, administer aspirin (patient should chew)
- If no contraindications, administer nitroglycerin
- Administer morphine, if needed
- Obtain 12-lead ECG
- Apply oxygen via nasal cannula if O2 <94%
3. Trained professional should assess ECG; ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
STEMI
- Complete fibrinolytic checklist
- Determine precise onset of symptoms, if possible
- Initiate Fibrinolysis/PCI protocol immediately
- Antiplatelet therapy
- Aspirin
- Platelet P2Y12 receptor blocker
- GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor (If destined for PCI)
- Anticoagulation
- Consider intravenous nitrates
- Consider morphine
- Beta-blockers (if no contraindications)
- Statin therapy
Non-ST elevation ACS (unstable angina or non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI))
- Antiplatelet therapy
- Aspirin
- Platelet P2Y12 receptor blocker
- Anticoagulation
- Admit to monitored bed
- Consult Cardiology
Mastering the Acute Coronary Syndrome Algorithm is essential for identifying and treating heart attacks quickly and effectively. Build the expertise and confidence to act fast and save lives with an online ACLS certification.