Are you a healthcare professional currently wondering if your ACLS certification is still valid? Missing your renewal window can lead to stress, missed shifts, or even non-compliance in your workplace. That’s why it’s important to know how long ACLS certification lasts and what you need to do to renew it.
This blog will break down everything you need to know about when ACLS certification expires, including renewal tips to make the process smooth and stress-free.
What Is ACLS Certification?
ACLS stands for Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. ACLS certification consists of a comprehensive course designed to teach healthcare professionals how to respond effectively to cardiac emergencies, such as cardiac arrest and stroke.
Once you have completed an online ACLS certification program, you will need to pass a written exam and a skills test in order to become certified. The written exam will test your knowledge of the ACLS guidelines, and the skills test will assess your ability to perform CPR and other lifesaving procedures.
ACLS certification is an important credential for healthcare professionals who work in emergency medicine. It demonstrates your commitment to providing high-quality care to patients in need.
How Long Is ACLS Good For?
ACLS certifications are valid for two years. After that, you will need to complete a recertification course to maintain your certification. This ensures that you stay updated on the latest lifesaving techniques when responding to cardiac emergencies.
Please note that some employers may have specific requirements regarding ACLS certification expiration dates. It’s important to check with your employer or organization for their specific policies.
Why Does ACLS Certification Expire?
Like many other certifications, ACLS certification expires to ensure that healthcare professionals stay current with the latest advancements in cardiac care.
Here are the primary reasons for this:
- Evolving Medical Practices:
- New guidelines and protocols: The field of medicine, particularly in emergency care, is constantly evolving. New research and clinical trials lead to updated guidelines and protocols for managing cardiac emergencies.
- Technological advancements: New medical devices and techniques are introduced regularly, requiring healthcare providers to be proficient in their use.
- Maintaining Skill Proficiency:
- Hands-on practice: Regular recertification courses provide opportunities for healthcare professionals to practice essential skills, such as intubation, defibrillation, and medication administration.
- Skill decay: Without regular practice, skills can deteriorate, potentially impacting patient outcomes.
- Ensuring Patient Safety:
- Competency assessment: Recertification processes help ensure that healthcare providers maintain the necessary knowledge and skills to provide high-quality care.
- Risk mitigation: By requiring regular updates, certification bodies aim to minimize the risk of errors and adverse events.
By mandating periodic recertification, healthcare organizations and regulatory bodies work to uphold standards of excellence in patient care and public safety.
How to Check Your ACLS Certification Expiration Date
- Check Your Certification Card:
- Look for the expiration date printed directly on your physical ACLS certification card.
- Contact Your Training Center:
- If you’re unsure where you got your certification or can’t find your card, contact the training center where you completed the course. They can provide you with the expiration date.
- Check Online Portals (if applicable):
- Some online certification platforms allow you to log in and view your certification details, including the expiration date.
Remember:
- ACLS certifications typically last for two years.
- It’s important to keep your certification valid to maintain your skills and eligibility to practice.
- Plan ahead for recertification to avoid any lapses in your certification status.
By following these steps, you can easily keep track of your ACLS certification expiration date and make sure you’re always prepared to provide the best possible care.
What Happens if Your ACLS Certification Expires?
If your ACLS certification expires, you will no longer be authorized to perform advanced cardiac life support procedures. This could have serious consequences, both professionally and legally.
Here are just some of the potential consequences of having an expired ACLS certification:
- Loss of Employment: Many healthcare facilities require their employees to maintain current ACLS certification as a condition of employment. If your certification expires, you may be subject to disciplinary action, including termination.
- Inability to Practice: If you are a healthcare provider, such as a nurse or physician, you may be unable to practice in certain settings or perform certain procedures if your ACLS certification has expired.
- Legal Liability: In the event of a medical emergency, if you attempt to provide advanced cardiac life support without a valid certification, you could be held liable for any harm that results from your actions.
- Difficulty Obtaining Future Certifications: Some certification boards may require you to complete additional training or testing if your certification has expired for an extended period.
To avoid these consequences, make sure to renew your certification before it expires.
How to Renew Your ACLS Certification
To renew your ACLS certification, you’ll typically need to complete a recertification course. Here are the general steps involved:
- Check Your Expiration Date:
- Confirm the exact expiration date on your current ACLS certification card.
- Enroll in a Recertification Course:
- Look for a reputable training provider such as ACLS Medical Training and enroll in their recertification course.
- Complete the Course Requirements:
- Online Learning Modules: Complete the required online modules at your own pace.
- Skills Check-Off: Demonstrate your proficiency in essential ACLS skills, such as CPR, defibrillation, and medication administration.
- Written Exam: Pass a written exam to assess your knowledge of ACLS guidelines and protocols.
- Receive Your New Certification Card:
- Upon successful completion of the recertification course, you will receive a new ACLS certification card with a valid expiration date.
Can I Renew My ACLS Certification Online?
Yes, you can! With ACLS Medical Training, you can renew your ACLS certification right from the comfort of your own home. Our ACLS Recertification Course is 100% online and mobile-friendly. Your progress will be tracked and saved automatically, so you can learn at your own pace. You will be provided with an updated ACLS provider card once you finish the program.
What Topics Are Covered in an ACLS Renewal Course?
An ACLS renewal course is designed to refresh your knowledge and skills in advanced cardiac life support. Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll typically learn during one of these courses:
- ACLS Algorithms: You’ll review the latest ACLS algorithms, which are step-by-step guidelines for managing cardiac arrest and other life-threatening arrhythmias.
- Pharmacology: You’ll review the appropriate use of medications in cardiac emergencies, including dosage, administration routes, and potential side effects.
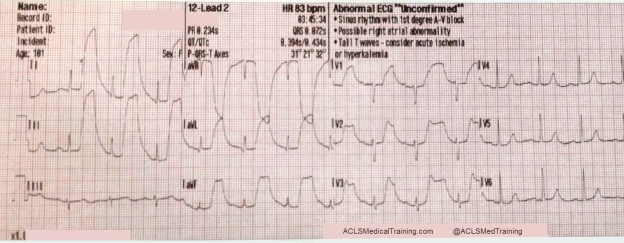
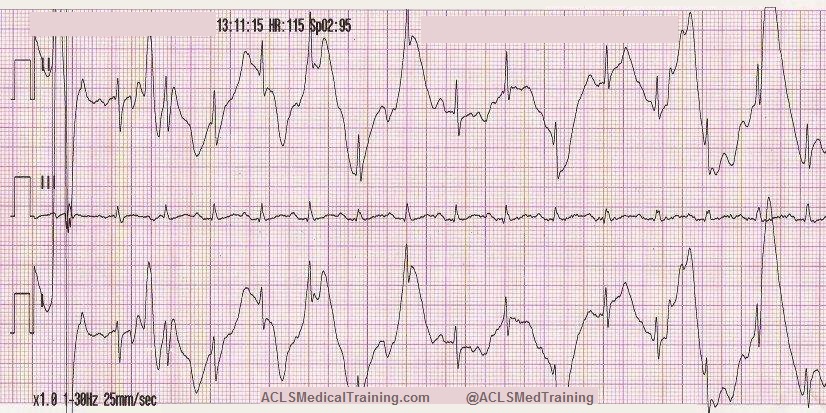
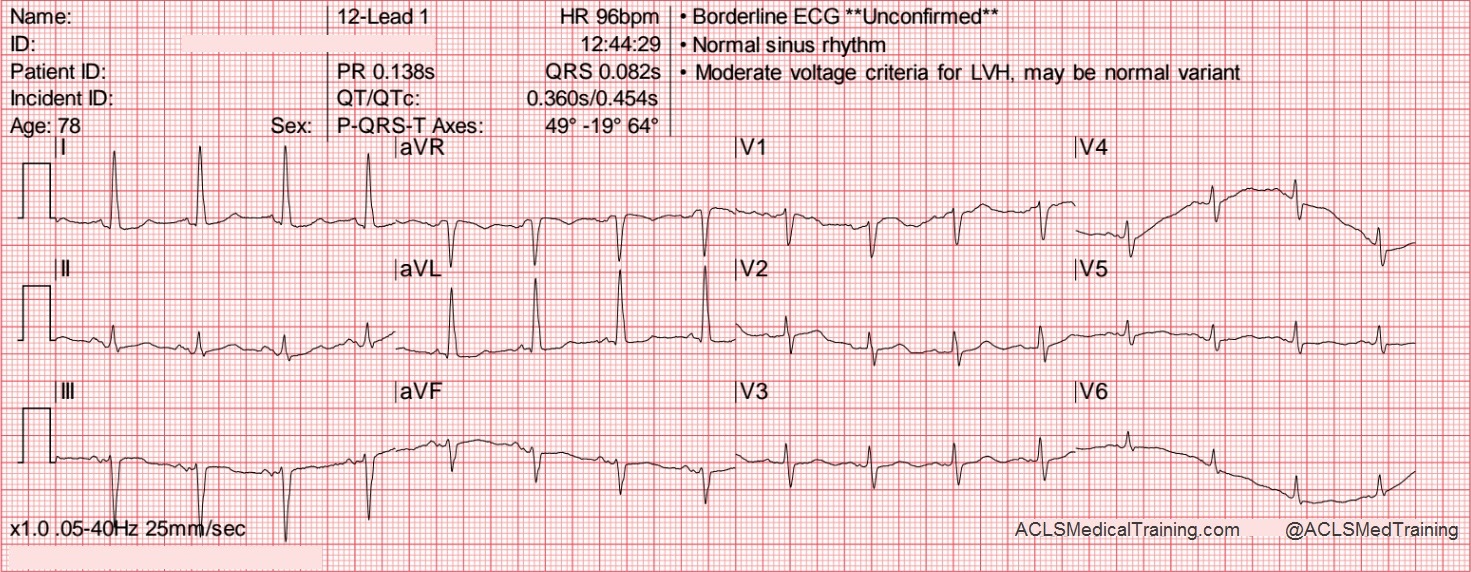
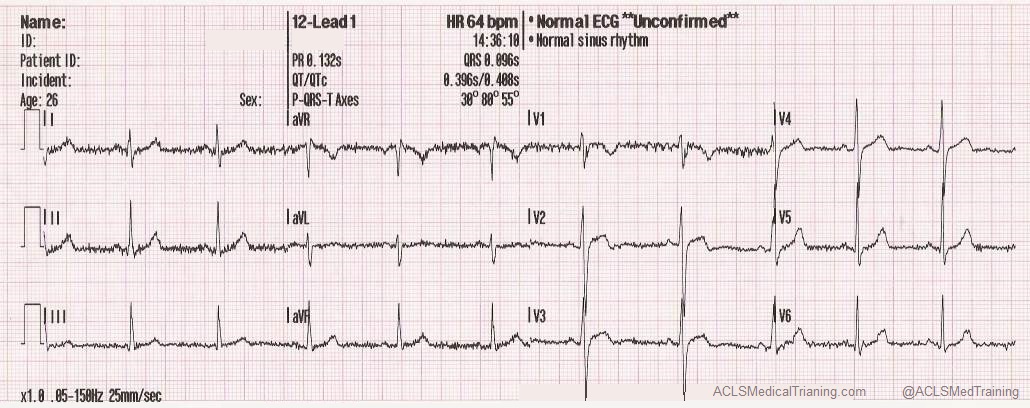
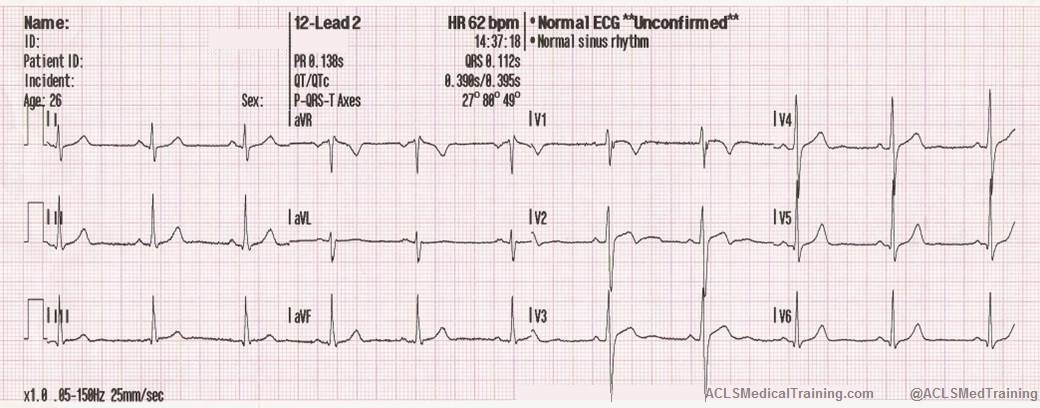
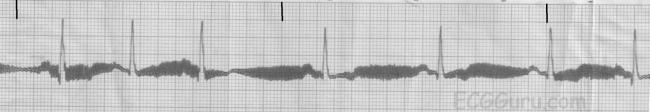
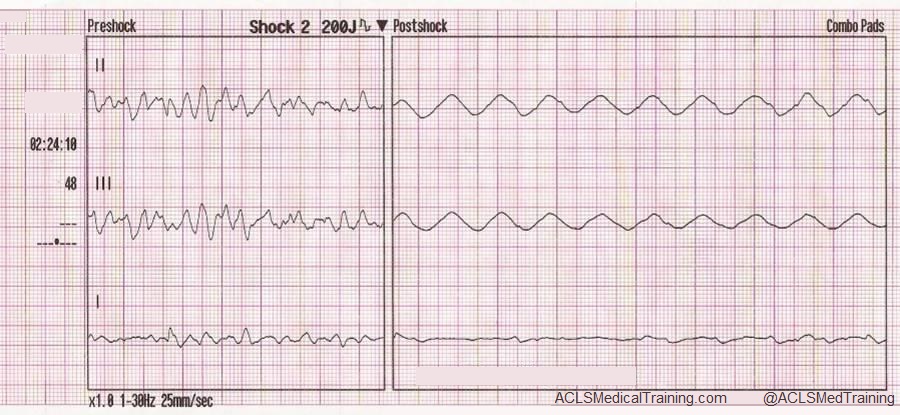
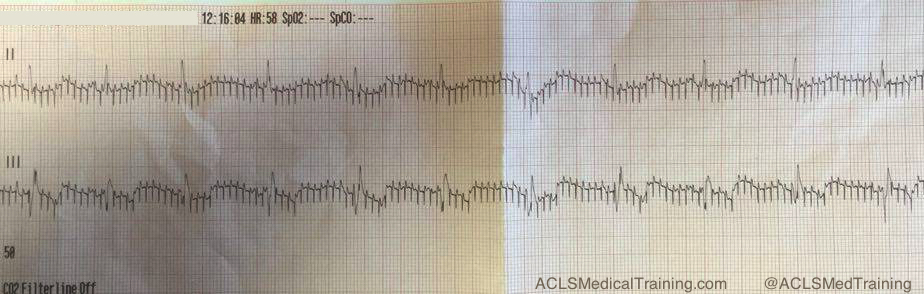
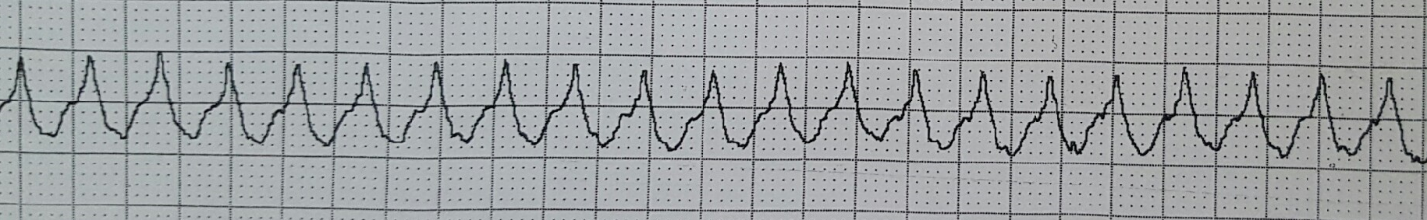
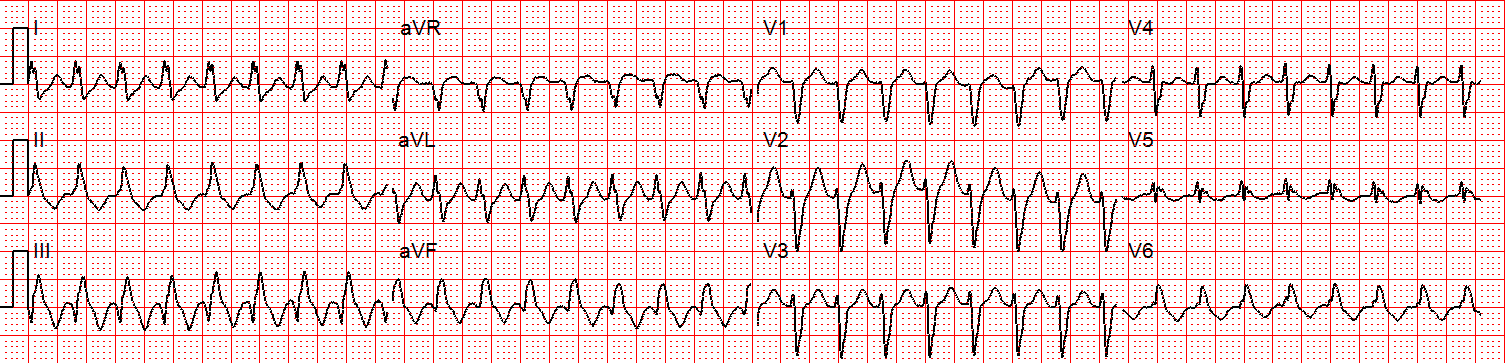
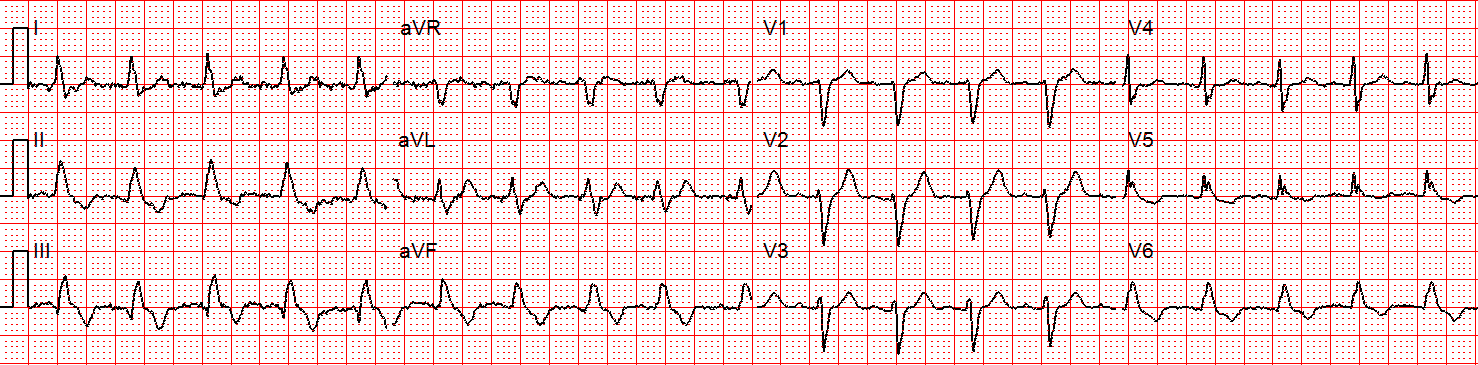
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) Interpretation: You’ll practice identifying and interpreting various cardiac arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and bradycardia.
Start Your Journey With ACLS Medical Training
Renewing your ACLS certification doesn’t have to be stressful. Whether you’re approaching your renewal date or getting certified for the first time, staying compliant ensures you’re always ready to save lives. Our online ACLS certification and recertification courses are designed to be convenient, comprehensive, and accessible. Enroll today and take the next step toward maintaining your lifesaving expertise!